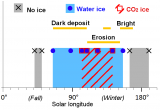
Ongoing flow activity was highlighted a few years ago on Mars by high-resolution cameras. Various flow types have been identified (new channels, dark lineae, bright deposits…) but there is still no consensus about possible formation mechanisms: dry avalanche? liquid water? carbon dioxide ice? A study conducted at the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale reveals for the first time the composition of winter ice forming in association with flows. Results suggest the coexistence of several current formation mechanisms.
Latest News
10 years 3 months ago
10 years 4 months ago
The stratospheric balloon carrying the PILOT instrument was launched from Timmins in Canada at 9 pm (local time) on Sunday, September 20th. The gondola, weighting more than a ton, the heaviest the CNES took in the last 25 years, was lifted by a stratospheric balloon of 800.000 m3 and reached the altitude of 39.500 m after 3 hours of ascent. After a last transfer of helium carried out just before take-off, the detectors reached nominally their operating temperature of 320 mK when the balloon reached its flight ceiling, and the scientific observations could then start.
10 years 4 months ago
The CLASP instrument (Chromospheric Lyman Alpha Spectropolarimeter) was successfully launched by a sounding rocket on September 3, 2015 at 17H UT from White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The suborbital flight was nominal. The instrument went nominally through its observing program and the data quality is superb.
10 years 4 months ago
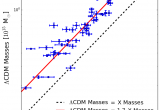
To reconcile the standard cosmological model with the X-ray measured number of galaxy clusters, a team of French scientists has shown that the cluster masses should be increased by 70% compared to current estimates. These results follow the conclusions obtained by the Planck mission in 2013 from observations of galaxy clusters in the microwave domain. This huge difference is intriguing: either our understanding of the physics of galaxy clusters needs to be revised, or the standard cosmological model is incomplete.
10 years 4 months ago
IAS is participating to the national open lab day "Fête de la Science" in the week of the 5th of October. After visits by students from several schools, the laboratory will be open for the general public on Sunday the 11th of October, from 2 to 6PM.
Here is the programme of activities and talks (in French) during this afternoon: