On the 3rd of December, the Japanese space agency has launched the Hayabusa 2 probe towards a primitive asteroid, named 1999JU3, that it will reach in 2018. This mission aims at analyzing this object in three complementary ways: in remote-sensing, with cameras and spectrometers; in-situ, with instruments on landers; and by laboratory analysis of samples that will be collected on the asteroid and returned to Earth in 2021.
You are here
Archive
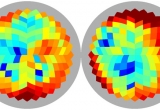
Beginning the 1st December at an international conference in Ferrara (Italy), the Planck collaboration, which involves the CNRS, the CEA, the CNES and several French universities among other institutes, reveals the results of four years of observation by the ESA Planck satellite of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), the oldest light in the universe. For the first time, the CMB is accurately measured on the whole sky in both its intensity and polarisation.
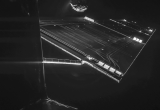
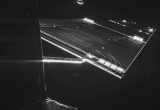
After a fascinating sequence, with a descent phase perfectly as planned and an impact at a few tens of metres from the selected site followed by two rebounds, Philae finally stopped in a hollow surrounded by cliffs, in an acrobatic position. It is the first panorama taken by the CIVA cameras developed under IAS responsibility which has demonstrated this, confirming the first major success of the mission: Philae has landed and has operated on the nucleus of comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko!
On October the 7th, one of the CIVA cameras took a new striking image of Rosetta with comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko in the background, at only 16 km. The CIVA instrument on the Philae lander (now still attached to the Rosetta orbiter) is a suite of cameras which were developed under IAS responsibility.
IAS is participating to the national open lab day "Fête de la Science" in the week of the 6th of October. After visits by students from several schools, the laboratory will be open for the general public on Sunday the 12th of October, from 2 to 6PM.
The Planck consortium has published a statistical analysis of the dust polarization towards the regions of the sky best suited to measure Cosmic Microwave Background polarization. This work shows that dust polarization is significant over all of the sky, and that the signature of cosmic inflation will not be detected unless contamination associated with the dusty and magnetized interstellar medium in the Galaxy is removed with the required accuracy and confidence.
The target region of Rosetta’s lander Philae has been selected: the site offers a unique scientific potential with hints of activity nearby, minimum risks to the lander and good conditions to exploit energy resources. Landing is scheduled for November 11.
Two months prior to its separation, descent, and landing on the Churyumov-Gerasimenko nucleus, the Philae lander of the ESA Rosetta mission delivers its first images of the comet. The 7 micro-cameras of the CIVA instrument, designed and developed under IAS responsibility, will acquire the full 360° panorama of the landing site.
Jean-Loup Puget, Directeur de Recherche at CNRS, working at Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, has received the 2014 Space Science Award of COSPAR (Committee on Space Research). This Award honors a scientist who has made outstanding contributions to space science.
The first collection of cometary dust is initiated for the COSIMA mass spectrometer on-board Rosetta
The COSIMA instrument on board the Rosetta spacecraft will provide the first high resolution mass spectra of grains collected close to a comet. The imaging system of COSIMA, COSISCOPE, built by Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale, will locate and characterize the collected cometary grains.